7 Essential Electrical Safety Tips Every Maricopa County Homeowner Must Know
Electricity powers our lives, but it requires respect and understanding to ensure our homes are safe and our families are protected. For homeowners in Maricopa County, Arizona, knowing the basics of your home’s electrical system is not just about convenience—it’s a necessity. Here’s a guide to help you navigate the electrical essentials, crafted with Maricopa County’s unique needs in mind.
The Ultimate Guide to Electrical Safety in Maricopa County
Understanding your home’s electrical system is crucial for safety, efficiency, and peace of mind. Below are seven key areas every homeowner should be familiar with:
Safety First: Navigating Your Electrical System
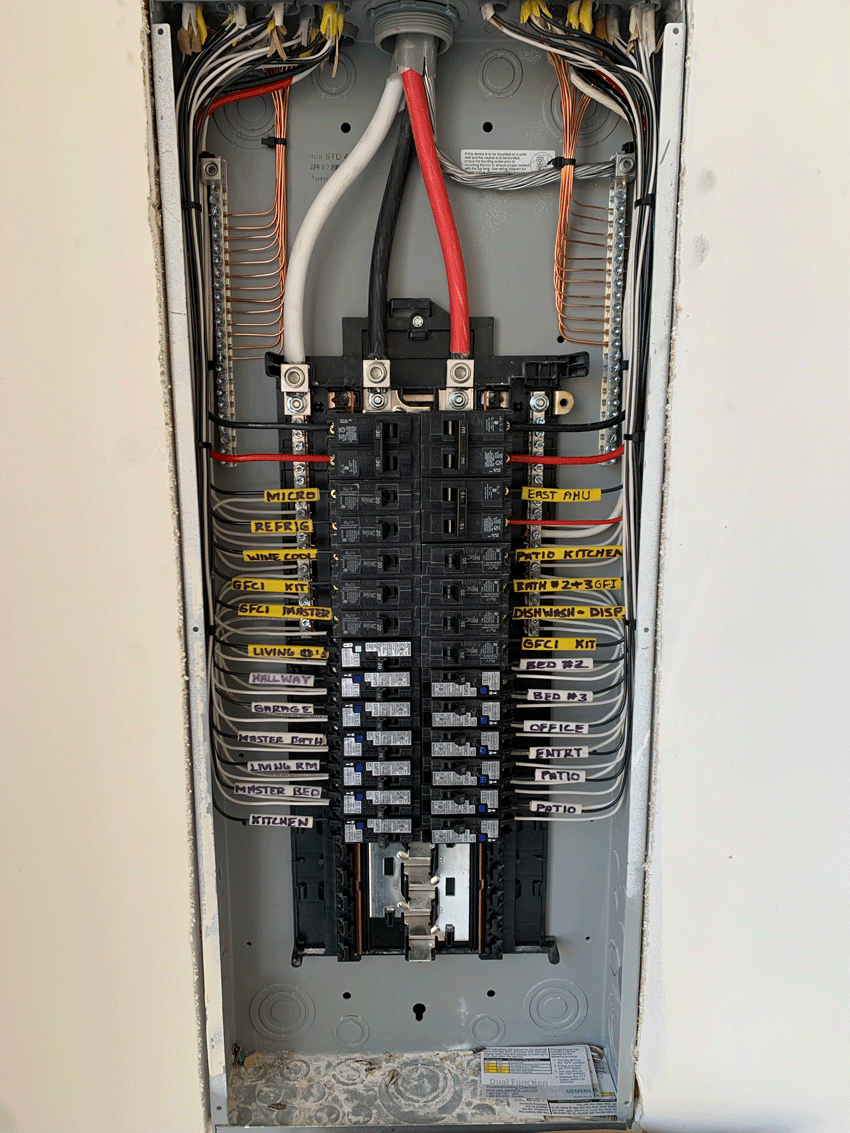
Identify Your Main Electrical Panel
Knowing the location of your main electrical panel, typically found in the garage, basement, or utility room, is the first step in electrical safety. It’s essential to understand how to shut off power to your entire home or individual circuits in an emergency.
Recognize Warning Signs
Flickering lights, hot outlets, a burning smell, or frequent breaker trips are clear indicators of potential electrical problems. These signs should not be ignored and require immediate attention from a professional electrician.
The Dangers of DIY Electrical Repairs
While DIY projects can be tempting, electrical repairs should only be performed by qualified professionals. The risks of improper work include fires, injuries, and even death.
Maintenance and Awareness for a Safe Home
Regular Electrical Inspections
Especially important for older homes or those undergoing renovations, scheduling regular inspections with a licensed electrician can prevent many electrical issues before they become serious.
Know Your Electrical Capacity
Understanding the electrical load your home can handle is key to preventing overloading circuits. This knowledge is particularly important when adding new appliances or technology to your home.
The Importance of GFCI Outlets
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets provide an extra layer of protection against electrical shock, especially in areas prone to moisture like bathrooms and kitchens. Ensure your home is equipped with these lifesaving devices.
Local Considerations and Additional Safety Measures
Maricopa County’s Electrical Codes
Familiarize yourself with local regulations and permit requirements for electrical work in Maricopa County. Compliance with these codes is crucial for both safety and legality.
Pool and Spa Electrical Safety
If your home includes a pool or spa, understanding the specific electrical safety requirements is essential. Proper bonding and grounding are non-negotiable to prevent shock hazards.
Take Action: Secure Your Home Today
Understanding your home’s electrical system and adhering to these safety guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents. If you’re in Maricopa County and need professional electrical services, don’t hesitate to reach out to State Electrical Contractors. We’re here to ensure your home is safe, efficient, and compliant with all local codes.
Ready to ensure your home is as safe as it can be? Contact State Electrical Contractors today for a comprehensive electrical safety inspection. Protect your home and loved ones with the expertise of Maricopa County’s most trusted electricians.
Local Electrical Expertise for Your Peace of Mind
Absolutely! Here at State Electrical Contractors, we’re all about keeping things crystal clear for our neighbors in Phoenix and Maricopa County. We offer no-charge estimates to help you plan your electrical upgrades or fixes without any surprises. Count on us for an upfront breakdown of costs, following a thorough site inspection to ensure pinpoint accuracy and full transparency.
Confused about Electrical Quotes vs. Estimates?
Don’t be left in the dark! Here’s the difference:
- Quote: A fixed price, like a menu. Great if you know exactly what you need, but not ideal for electrical work where surprises can lurk behind the walls.
- Estimate: A ballpark figure based on experience. It gives you a clear idea of the cost range, with room to adjust if we uncover any hidden issues during the inspection.
Why an Estimate is Better for Electrical Work:
- Peace of Mind: No hidden costs! We’ll adjust the estimate if unexpected problems arise, keeping you informed every step of the way.
- Accurate Pricing: Our estimates consider potential challenges, ensuring a fair and realistic price for a safe and functional electrical system.
- Flexibility: Need to add outlets or troubleshoot an unknown issue? An estimate allows us to adapt to your project’s needs without breaking the bank.
You bet! Our team isn’t just skilled; we’re fully licensed and insured, offering top-notch services across the Phoenix area and Maricopa County. Our credentials and comprehensive insurance mean you can rest easy knowing you’ve got professionals committed to safety and excellence working for you.
From the heart of Phoenix to every corner of Maricopa County, our electricians are here for you. Our deep roots and extensive local knowledge position us as your first choice for any electrical project, no matter the size.
Area we serve include but are not limited to:
- Apache Junction
- Carefree
- Cave Creek
- Chandler
- Chandler Heights
- Fort McDowell
- Fountain Hills
- Gilbert
- Glendale
- Gold Canyon
- Higley
- Mesa
- Paradise Valley
- Peoria
- Phoenix
- Queen Creek
- Rio Verde
- San Tan Valley
- Scottsdale
- Tempe
- Tortilla Flat
- Pinnacle Peak
With years of service under our belts, we’ve established ourselves as a trusted name in Arizona’s electrical industry. Our longevity speaks to our commitment to reliable service and customer satisfaction. Our master electricians have over 35 years of experience.
Combined, we provide a multi-generational volume of knowledge and expertise. Our extensive experience, spanning several decades in the industry, underlines our capabilities and results. Trust is paramount, and our longstanding presence in Arizona is a testament to our quality service and customer satisfaction.
Day or night, weekday or weekend, we’re on call to address your electrical needs. Our around-the-clock availability ensures that we’re here for you whenever you need us, be it for an unexpected outage or a scheduled project.
Our local electrician here at State Electrical Contractors will accept a variety of payment options. We strive for convenience, accepting a range of payment methods including credit cards, checks, and online transactions. It’s all about making your experience with us as smooth and hassle-free as possible.
Solutions Tailored to Your Needs
Flickering lights can signal anything from minor bulb issues to more serious wiring concerns. Let our experts take a closer look to diagnose and resolve the issue safely and effectively.
Our local electricians will check:
Common Causes:
- Loose Connections: Vibrations or settling of the house can loosen connections in outlets, switches, or the main electrical panel, causing flickering.
- Overloaded Circuit: Using too many appliances on one circuit can overload it, leading to flickering lights and potentially tripped breakers.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Utility power fluctuations can cause momentary dimming or flickering across your entire home.
- Failing Light Bulb: A loose filament or nearing the end of its lifespan can cause a bulb to flicker before burning out completely.
- Aging Wiring: Older homes in Maricopa County might have outdated wiring that cannot handle the increased electrical demands of modern appliances, leading to flickering.
Additional Considerations:
- Dimmers: If the flickering only occurs with dimmer switches, the dimmer itself might be faulty.
- Appliance Usage: Notice if the flickering happens when using specific appliances, as it could indicate a problem with the appliance or the circuit it’s on.
Recommendations:
- Safety First: If flickering is accompanied by burning smells, sparks, or tripping breakers frequently, turn off the power and contact a qualified electrician immediately.
- Check for Loose Bulbs: Tighten any loose bulbs in the affected fixtures.
- Reduce Electrical Load: Try unplugging non-essential appliances from the circuit experiencing flickering.
- Contact a Licensed Electrician: If the above suggestions don’t resolve the issue, or you’re unsure about the cause, it’s crucial to consult one of our licensed electricians for proper diagnosis and repair to ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical system.
Remember, flickering lights can indicate underlying electrical problems that require professional attention. Ignoring them can pose safety hazards and lead to more extensive issues in the future.
Certainly! Ceiling fan installations are one of our specialties. We ensure your new fan is both aesthetically pleasing and optimally functional, adding comfort and efficiency to your space.
Upgrading your electrical panel is key to ensuring safety and accommodating modern appliances. Our team can evaluate your current setup and recommend the ideal upgrade to enhance your home’s functionality and safety.
Outdoor Living, Enhanced
While some minor problems can be safely managed, electrical work is generally best left to the pros. For your safety, we’re here to guide you through any minor troubleshooting or to take on the more complex challenges directly.
If you’re experiencing flickering lights, sparking outlets, or detect a burning smell, it’s time to call us. These issues could point to serious hazards that need expert attention right away.
Electrical Terms You May Encounter
The central distribution point for electrical circuits in a building, often known as a breaker panel or distribution board. It houses circuit breakers and distributes electricity to various areas of the property. Circuit panels are essential for managing and safeguarding the electrical system in both residential and commercial settings.
Circuit panels are known by several terms in the electrical and engineering fields. Here is a list of circuit panel terms you may have encountered:
- Distribution Board
- Electrical Panel
- Breaker Panel
- Panelboard
- Fuse Box
- Consumer Unit
- Electrical Distribution Board
- Switchboard
- Electrical Control Panel
- Load Center
- Service Panel
- Electrical Service Panel
- Circuit Breaker Box
- Power Distribution Board
- Main Panel
- Subpanel
- Electrical Cabinet
- Switchgear
- Meter Panel
- Distribution Box
These terms may vary by region, industry, and specific application, but they all refer to devices that distribute electrical power to various circuits.
An automatic electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. It interrupts current flow after detecting a fault, ensuring the safety of the electrical system. Circuit breaker installation and replacement are critical services for maintaining electrical safety.
The process of replacing an old electrical panel with a new one to accommodate additional circuits and ensure safety. Upgrading the electrical panel is crucial for properties with increased electrical demands, such as those installing new appliances or expanding their home or business.
A thorough examination of the electrical system by a licensed electrician to ensure it meets local safety codes and standards. Regular electrical inspections can prevent potential hazards, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance with electrical codes.
A device that supplies electric energy to recharge electric vehicles. EV chargers can be installed in homes, businesses, and public locations.
Devices or systems designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. Surge protectors divert excess voltage to the ground to prevent damage.
A detailed schematic that shows the layout and connections of an electrical system. Wiring diagrams are essential for troubleshooting, repairs, and understanding the electrical setup of a property.
A safety measure that involves connecting the electrical system to the earth to prevent electric shock and damage during electrical faults. Proper grounding is vital for the safety of any electrical installation.
An older type of electrical panel that uses fuses instead of circuit breakers to protect circuits. Fuses must be replaced when they blow, unlike circuit breakers which can be reset. Fuse boxes are often found in older homes and may need to be upgraded to modern circuit breaker panels for enhanced safety.
A device that shuts off an electric power circuit when it detects current flowing along an unintended path, such as water or a person. GFCIs are essential for areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens, to prevent electric shock.
A circuit breaker that detects electrical arcs and shuts off the circuit to prevent electrical fires. AFCIs are particularly important in residential settings to protect against arc faults in electrical wiring.
The process of determining the total electrical load required by a building. Proper load calculations ensure the electrical system can handle the demand without overloading, which is crucial for planning electrical installations and upgrades.
The unit of measure for electric current. It indicates how much electricity flows through a circuit. Understanding amperage is essential for selecting the right electrical components and ensuring system compatibility.
The unit of measure for electric potential difference. It indicates the force that drives electric current through a circuit. Voltage ratings are critical for ensuring the safe operation of electrical devices.
A unit of energy representing one kilowatt of power used for one hour. It’s commonly used by electric utilities to measure energy consumption. Monitoring kWh usage helps in managing electricity costs and efficiency.
Understanding Kilowatt-Hours (kWh) in Maricopa County, AZ
Kilowatt-Hour (kWh) Explained: A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy used to measure electricity consumption. It represents the amount of energy consumed when a 1,000-watt appliance runs for one hour. For example, if you use a 100-watt light bulb for 10 hours, you have used 1 kWh of energy (100 watts * 10 hours = 1,000 watt-hours = 1 kWh).
Average Cost of a kWh in Maricopa County, AZ: As of the most recent data, the average cost of electricity in Maricopa County, AZ, is approximately $0.12 per kWh. This rate can vary slightly depending on the specific utility provider, the season, and the overall demand for electricity.
Why kWh Matters to Homeowners and Businesses: Understanding kWh is essential for managing electricity usage and costs. Here’s how it affects you:
- Monthly Electric Bills:
- Your electric bill is calculated based on the total number of kWh you consume each month. By knowing the cost per kWh, you can estimate your monthly electricity expenses and budget accordingly.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Monitoring kWh usage helps you identify which appliances or systems are consuming the most energy. This information is valuable for making decisions about upgrading to more energy-efficient models or implementing energy-saving practices.
- Cost Savings:
- Reducing kWh consumption directly translates to lower electric bills. Simple changes, such as using LED bulbs, unplugging devices when not in use, and adjusting thermostat settings, can significantly reduce your energy usage.
- Environmental Impact:
- Lower kWh consumption reduces your carbon footprint. By using less electricity, you contribute to environmental conservation and sustainability efforts.
Average kWh Consumption: To give you a better idea of average consumption, here are some typical usage patterns:
- Residential:
- The average household in Maricopa County consumes about 1,000 kWh per month. This includes energy used for lighting, heating, cooling, appliances, and electronics.
- Commercial:
- Small businesses may consume around 5,000 to 10,000 kWh per month, while larger commercial establishments can use significantly more, depending on their operations and energy needs.
Ways to Manage and Reduce kWh Usage:
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances:
- Look for appliances with the ENERGY STAR label, which indicates they meet energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
- Smart Thermostats:
- Installing a smart thermostat can help you manage heating and cooling more efficiently, adjusting temperatures based on your schedule and preferences.
- LED Lighting:
- Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs, which use less energy and have a longer lifespan.
- Energy Audits:
- Conduct an energy audit of your home or business to identify areas where you can improve efficiency and reduce consumption.
- Solar Panels:
- Consider investing in solar panels to generate your own electricity, reducing reliance on the grid and potentially lowering your kWh consumption and costs.
By understanding what a kilowatt-hour (kWh) means and how it impacts your electricity costs, you can make informed decisions about energy usage and savings in Maricopa County, AZ. Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner, managing your kWh consumption is key to controlling expenses and promoting sustainability.
Electrical services provided in homes, including wiring, panel upgrades, lighting installation, and repairs. Residential services ensure that home electrical systems are safe, efficient, and up to code.
Electrical services provided in commercial buildings, such as offices, stores, and factories. These services include installation, maintenance, and upgrades of electrical systems tailored to the specific needs of businesses.
Routine inspection and repair of electrical systems to ensure safety and efficiency. Regular maintenance can prevent major issues, extend the lifespan of electrical components, and ensure continuous operation.
Ensuring that all electrical installations and repairs meet local and national electrical codes, which are designed to ensure safety and reliability. Compliance is crucial for legal and insurance purposes.
A smaller service panel that distributes power to a specific area of a building. Subpanels are useful for extending the electrical system and reducing the load on the main panel.
The process of diagnosing and resolving electrical problems. Troubleshooting can involve identifying faulty circuits, broken components, or wiring issues. Professional troubleshooting is essential for maintaining the safety and functionality of electrical systems.
A device that supplies electric energy to recharge electric vehicles. EV chargers can be installed in homes, businesses, and public locations to support the growing adoption of electric vehicles.
The most basic EV charger, which uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. It provides slow charging and is suitable for overnight charging at home.
A faster EV charger that uses a 240-volt outlet, similar to what is used for large appliances like dryers. It significantly reduces charging time compared to Level 1 chargers and is ideal for home or business installations.
An advanced EV charger that provides rapid charging using direct current (DC). It can charge an EV to 80% in about 30 minutes, making it ideal for public charging stations and high-traffic areas.
A designated area equipped with EV chargers where electric vehicles can be recharged. Charging stations can be found in residential areas, commercial properties, and public spaces, supporting the infrastructure for EVs.
The physical plug that connects the EV to the charger. Different EVs may use different types of connectors, such as J1772 for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, or CCS and CHAdeMO for DC fast charging.
The inlet on an electric vehicle where the connector is plugged in to charge the battery. Charging ports vary by vehicle model and must be compatible with the charger.
A unit of power used to measure the rate at which electricity is being used. In the context of EVs, it’s often used to describe the power output of a charger.
The distance an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge. Range varies depending on the battery capacity and the efficiency of the vehicle, making it a critical consideration for EV owners.
A system that manages the battery pack of an EV, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity. It monitors the state of charge, temperature, and health of the battery.
The current charge level of an EV’s battery, expressed as a percentage of the total capacity. It indicates how much energy is left in the battery and helps drivers plan their trips.
An EV charger installed at a residential property, allowing homeowners to charge their electric vehicles conveniently at home. Home charging stations are crucial for the practical use of EVs.
An EV charger with advanced features such as remote monitoring, scheduling, and integration with renewable energy sources. Smart chargers optimize charging based on electricity rates and grid demand.
A vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine with a battery that can be recharged by plugging into an external source of electric power. PHEVs offer the flexibility of using both electricity and gasoline.
The distance a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle can travel solely on electric power before switching to its internal combustion engine. AER is a key performance metric for PHEVs.
Devices or systems designed to protect electrical equipment from voltage spikes by diverting excess voltage to the ground. Surge protection is essential for preventing damage to sensitive electronics.
A device that shields electronic devices from power surges. Surge protectors typically come in the form of power strips or installed units in electrical panels. They are crucial for safeguarding home and office electronics.
A device used to protect electrical power systems by diverting excess voltage from lightning strikes or internal surges to the ground. Surge arresters are critical for protecting large electrical systems.
A sudden increase in voltage that can damage electrical devices. Voltage spikes can be caused by lightning, power outages, or electrical faults, making surge protection vital.
A backup power system that provides electricity to an entire home during a power outage. Whole home generators are typically powered by natural gas or propane and are connected directly to the home’s electrical system to automatically supply power when the main power source fails.
Whole home generators are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages. Here’s a comprehensive list of all the terms that can refer to a whole home generator:
- Standby Generator:
- A generator that remains on standby mode and automatically activates during a power outage to supply power to the entire home.
- Backup Generator:
- A generator used as a backup power source to provide electricity when the main power supply fails.
- Home Standby Generator:
- Specifically designed for residential use, this generator ensures a continuous power supply during outages.
- Residential Generator:
- A general term for generators used in homes to provide backup power during emergencies.
- Automatic Generator:
- Refers to generators that automatically turn on and off based on the power status, ensuring seamless power transition during outages.
- Emergency Generator:
- A generator used in emergency situations to provide power when the primary source is unavailable.
- Whole House Generator:
- Similar to a whole home generator, this term emphasizes providing power to the entire house during an outage.
- Permanent Generator:
- A fixed, permanent installation designed to provide reliable backup power for a home.
- Home Backup Generator:
- Another term for generators specifically installed to provide backup power to residential properties.
- Automatic Standby Generator:
- Combines the features of automatic activation and standby mode, ensuring reliable backup power.