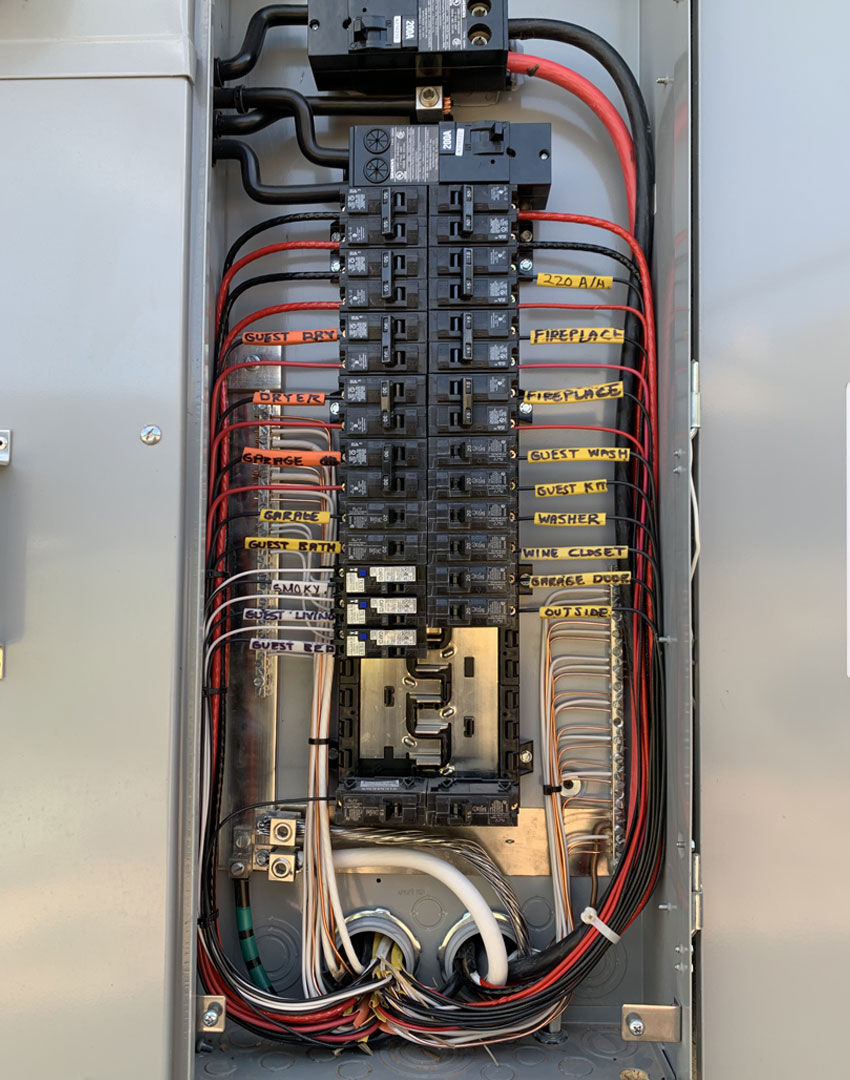
Understanding Your Circuit Panel:
A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to the ultimate guide to understanding, maintaining, and upgrading your home’s circuit panel system, tailored specifically for residents of Maricopa County. Whether you are dealing with an outdated fuse box, planning a major renovation, or simply aiming to enhance your home’s electrical safety, this guide provides you with all the necessary information. We’ll cover the essentials of your electrical system, signs that indicate a need for an upgrade, how to choose the right electrician, and much more. Designed to empower homeowners with knowledge and practical tips, this guide ensures you can manage your electrical needs with confidence.
Safety Warning for Maricopa County Residents
If you notice a burning smell from electrical devices or outlets, burn marks, sparking sounds, frequent tripping of breakers, or flickering lights, STOP AND CALL ONE OF OUR ELECTRICIANS IMMEDIATELY. These signs indicate serious electrical issues that need immediate attention.
Schedule an electrical inspection if your home is over 25 years old, recently purchased, undergoing renovations, or experiencing frequent electrical problems. Unexplained increases in your electricity bill also warrant an inspection.
Always Stay safe, Maricopa County!
- Circuit Panel Types:
- Part 1: Introduction to Your Home’s Electrical System
- Part 2: Identifying and Understanding Your Circuit Panel
- Part 3: Signs You Need a Circuit Panel Upgrade
- Part 4: Upgrading Your Circuit Panel: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
- Adding a Subpanel
- Part 5: Maintenance Tips for Your Electrical Panel
- Part 6: Advanced Considerations for Your Electrical System
- Part 7: Local Laws and Codes in Maricopa County
- Part 8: FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide
- Part 9: Glossary of Terms and Resources
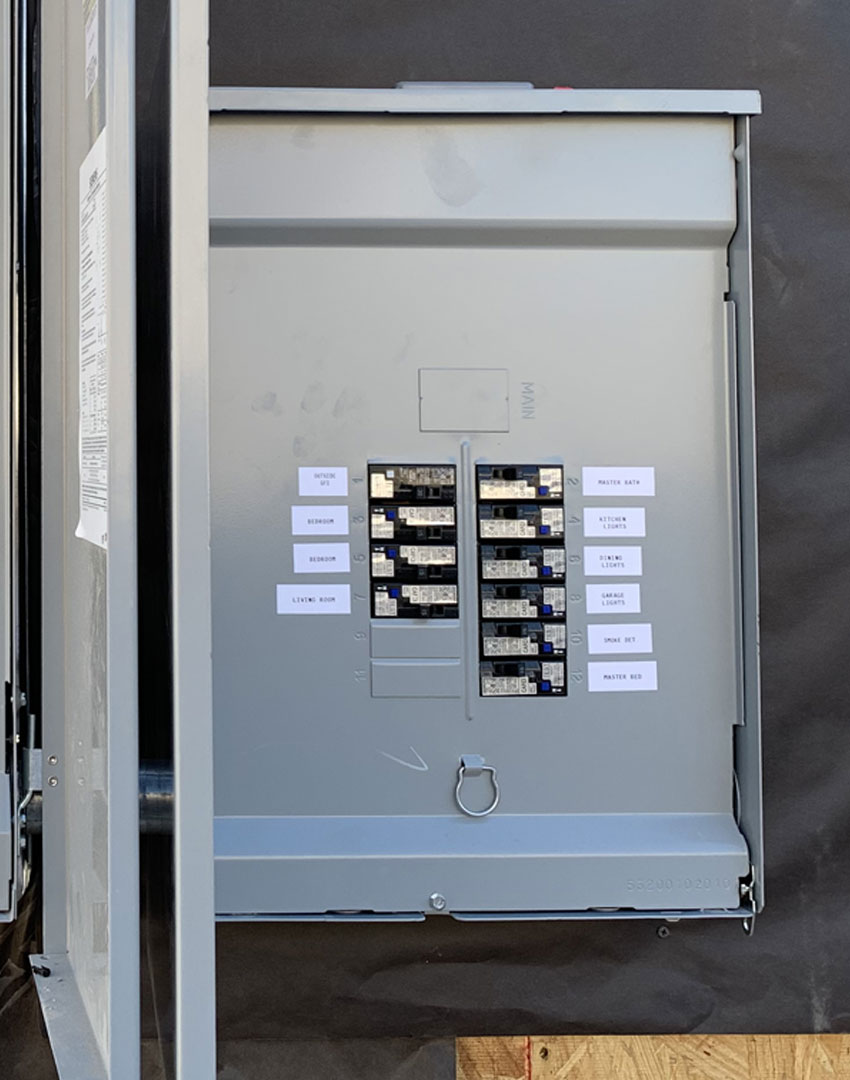
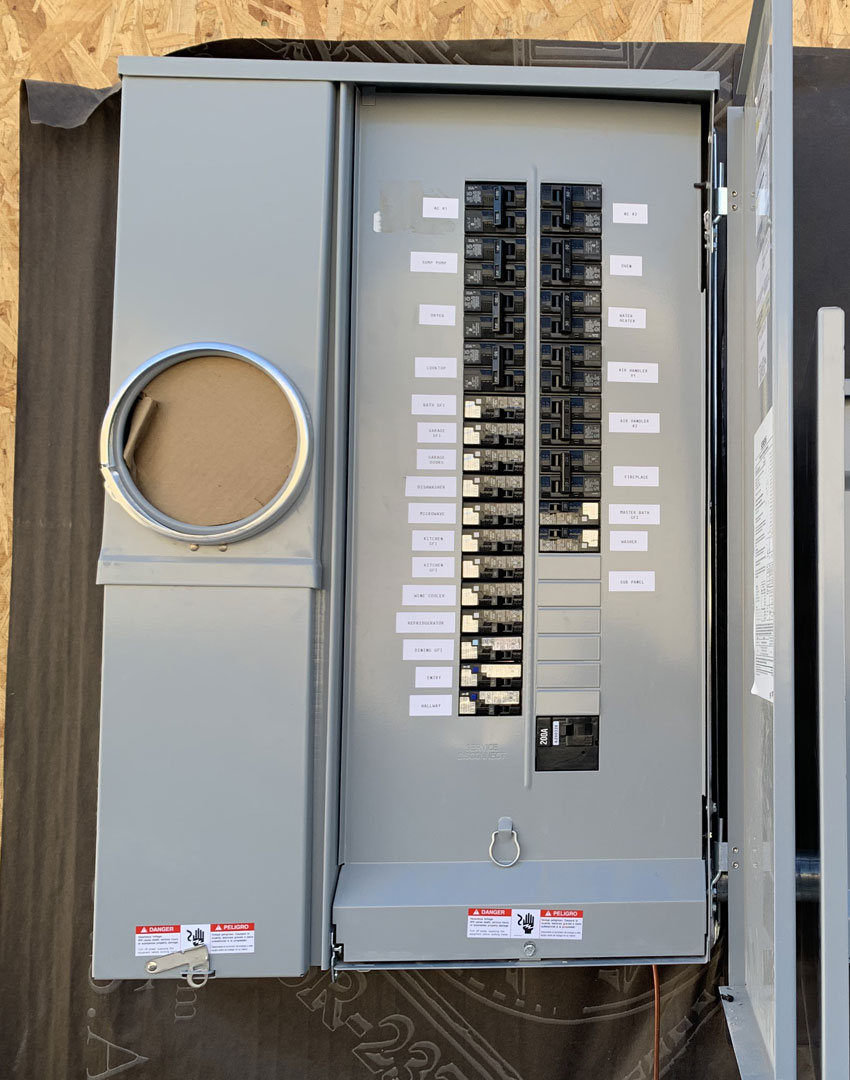
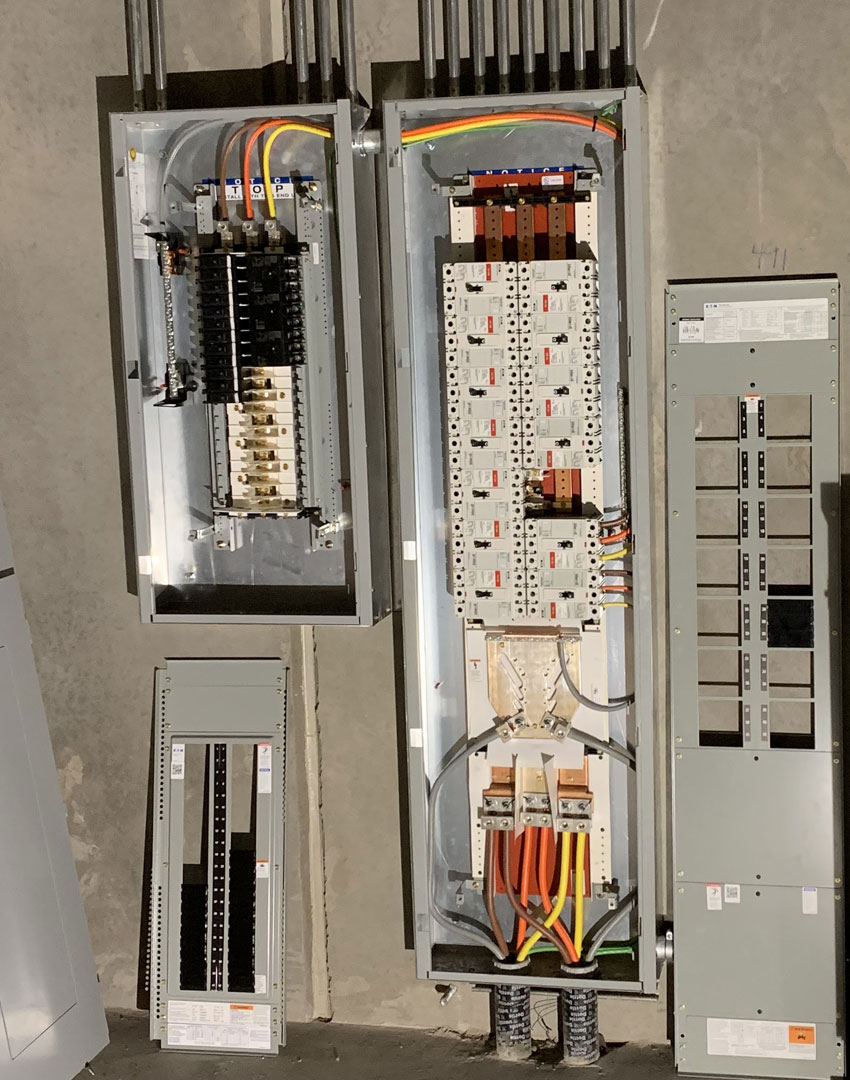
Circuit Panel Types:
In Maricopa County, Arizona, common types of circuit panels you might encounter include:
Main Breaker Panels:
- Standard: These have a main breaker to shut off power to the whole house and individual breakers for circuits.
- Split-Bus: These have two separate sections of breakers, sometimes for different areas of the house.
Main Lug Panels:
- Used more in commercial settings, they don’t have a main breaker and connect directly to the power lines.
Subpanels:
- Smaller panels branching off the main one, often for specific areas like garages or additions.
Transfer Switches:
- Not exactly a panel, but a device that lets you switch between the main power and a backup generator.
Older homes may still have:
- Fuse Boxes: These use fuses instead of breakers, and are generally outdated.
Specific brands/models vary, but these are the broad categories you’ll deal with when doing electrical work in the area.

Part 1: Introduction to Your Home’s Electrical System
Overview: Understanding Your Electrical System and Its Components
At the heart of your home’s electrical system is the circuit panel, which functions as the main control center for distributing electricity throughout your home. This system comprises various components, each playing a critical role in ensuring efficient and safe power distribution. Here’s a brief overview of these key components:
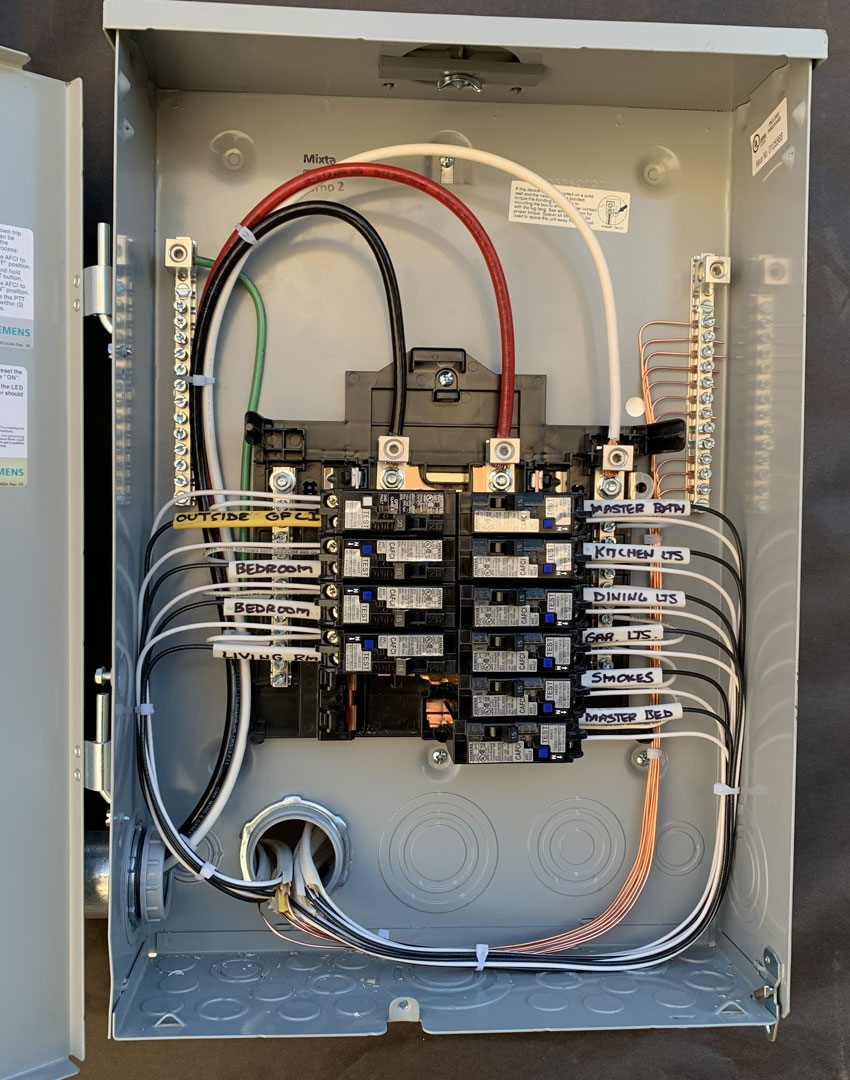
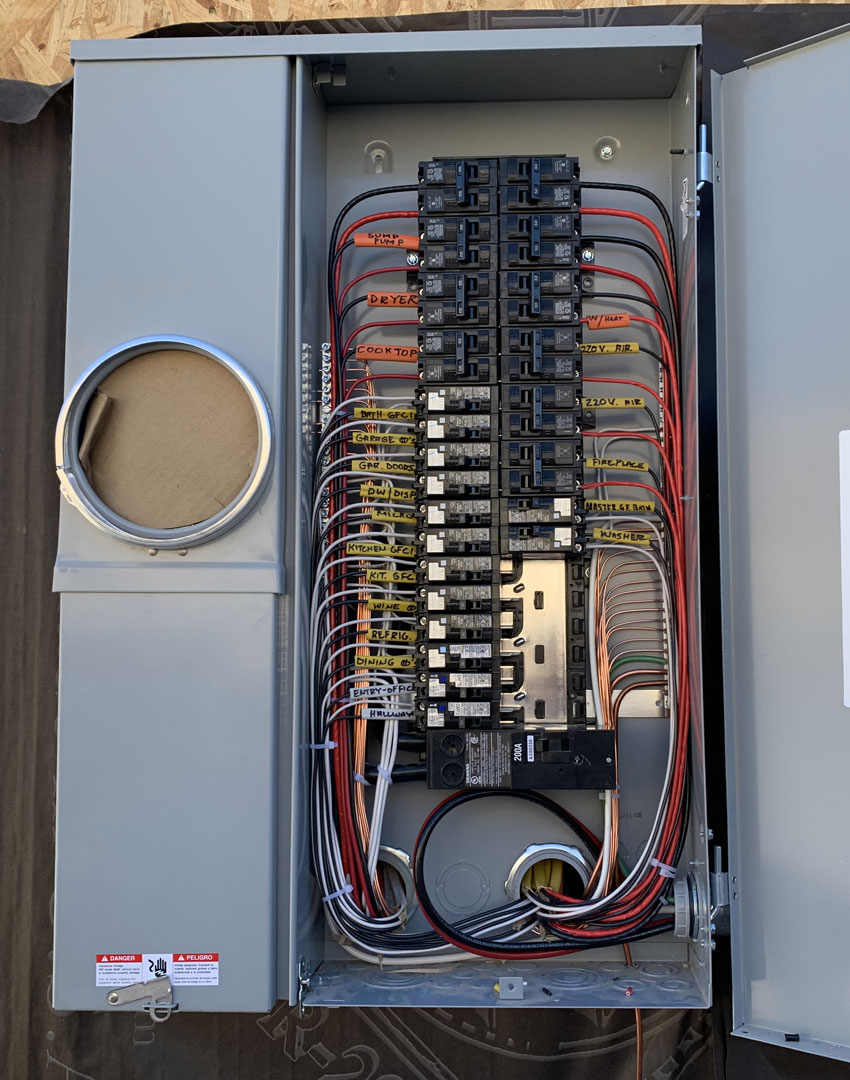
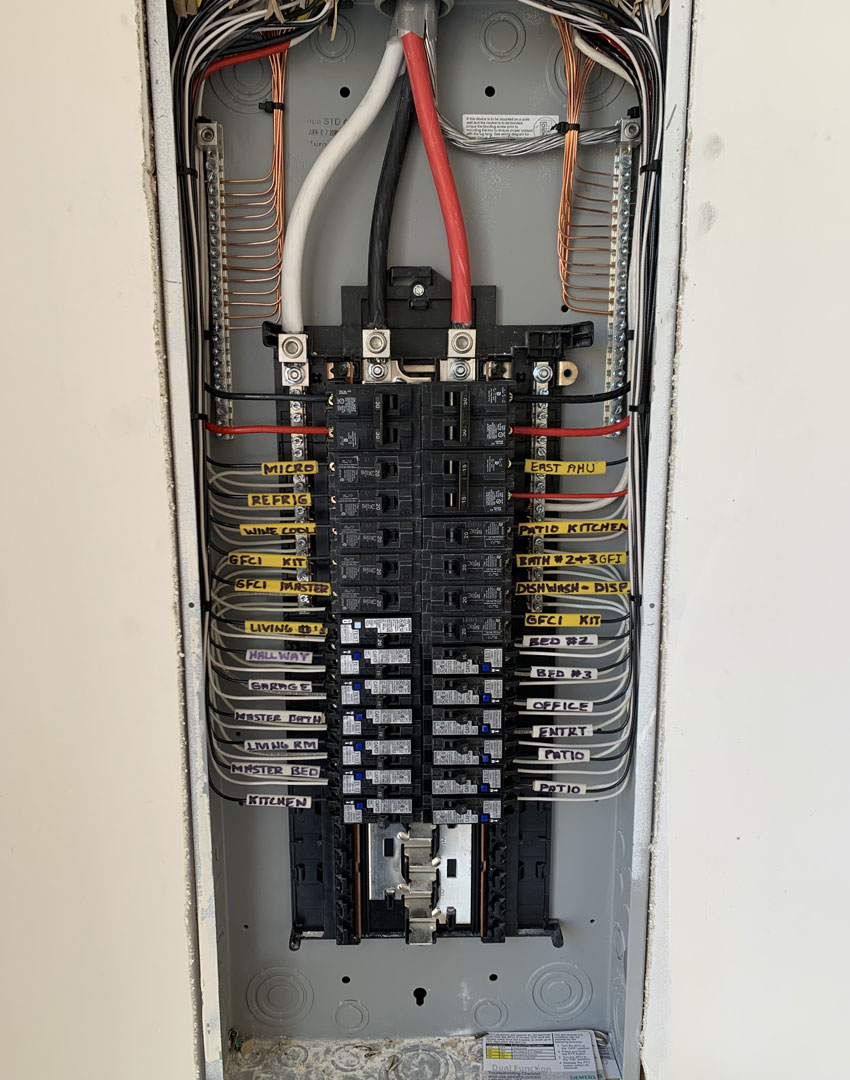
- Circuit Panel (Breaker Panel): This is where the electrical supply is managed and distributed. It contains circuit breakers or fuses that automatically shut off power when a system overload is detected, preventing potential fires or damage.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: These are safety mechanisms that stop electrical flow whenever an overload or short circuit occurs, protecting the wiring and preventing fires.
- Main Disconnect: A switch that can shut off the power to the entire house. This feature is crucial for safety during emergencies or maintenance.
- Bus Bars: Conduct electricity within the panel, distributing power to each circuit breaker.
- Neutral Bar: A grounding point for circuits in the breaker panel.
- Grounding Rod: A rod made of metal, driven into the ground to direct unwanted electrical charges away from your home to prevent electrical shocks.
The electrical panel processes incoming electricity from the utility company and distributes it through various circuits to different parts of your house. Each circuit is protected by a breaker or fuse that will cut off the power if too much electricity flows through it, thus preventing potential hazards.


Part 2: Identifying and Understanding Your Circuit Panel
Types of Circuit Panels: Fuse Boxes vs. Modern Circuit Breaker Panels
The type of circuit panel in your home is crucial for managing power and protecting against electrical hazards. Here’s a quick look at the two main types of panels: fuse boxes and modern circuit breaker panels.
Fuse Boxes
If you live in an older home, you might have a fuse box. These panels use fuses containing a thin metal strip that melts and disconnects when the current exceeds a safe level. While fuse boxes are effective, they come with some drawbacks:
- Replacement Required: When a fuse blows, it must be replaced, which can be inconvenient and costly over time.
- Safety Concerns: Incorrectly replacing fuses can lead to potential hazards, making fuse boxes less safe compared to modern alternatives.
Circuit Breaker Panels
Modern homes typically feature circuit breaker panels, which offer several advantages over fuse boxes:
- User-Friendly: Circuit breakers are switches that automatically trip (turn off) when they detect an overload or short circuit, protecting your wiring and preventing fires.
- Easy Reset: Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be easily reset without needing replacement, making them more practical for today’s electrical demands.

Part 3: Signs You Need a Circuit Panel Upgrade
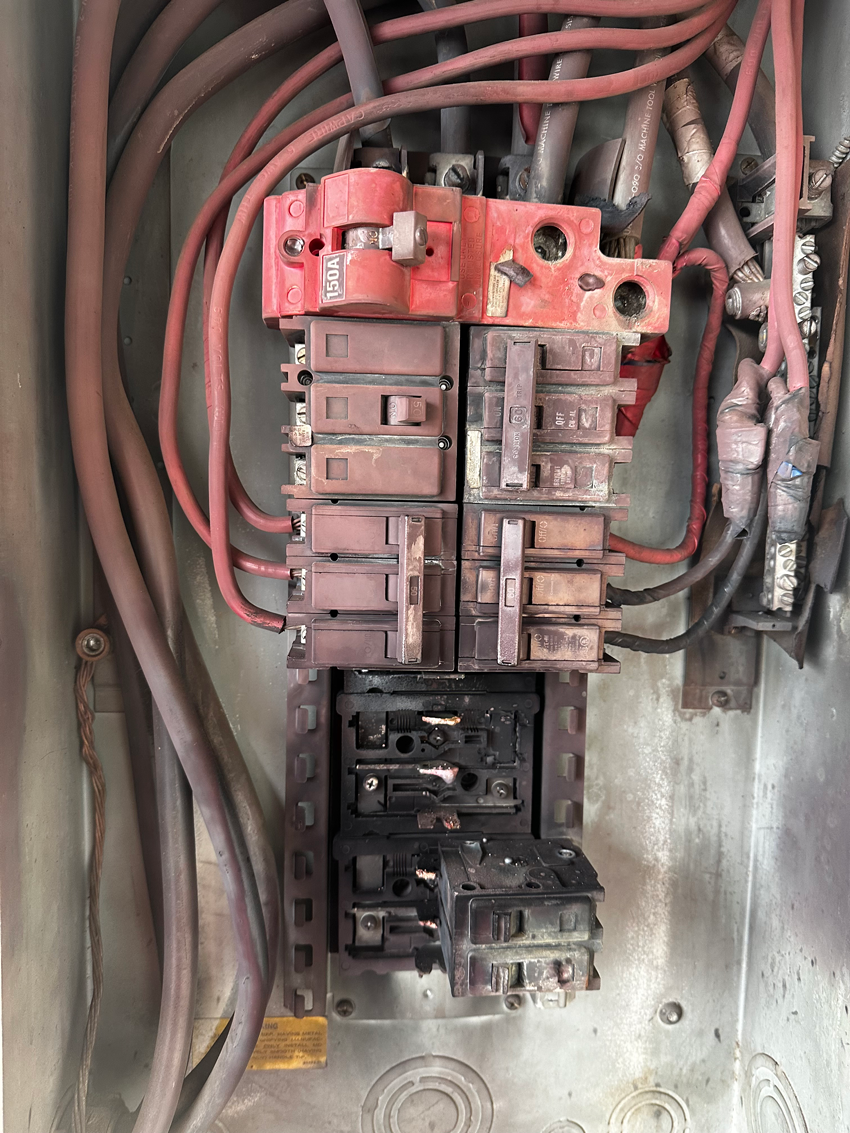
Aging Infrastructure: The Risks Associated with Old Electrical Panels
As your home ages, so does its electrical infrastructure, including the circuit panel, which is central to your home’s electrical system. Older panels, especially those installed by brands like Federal Pacific or Zinsco, are notorious for their safety hazards and inefficiencies. Here’s what you need to know about the risks:
- Federal Pacific Panels: These panels were commonly installed from the 1950s to the 1980s. They are known for having defective breakers that fail to trip in the event of an overload. This defect significantly increases the risk of fires and has led to several incidents over the decades.
- Zinsco Panels: Similar to Federal Pacific, Zinsco panels were popular during the mid-20th century. These panels can corrode and overheat without tripping the breaker, posing a fire hazard. Moreover, the breakers might appear to be off but still allow power through, creating a risk of electrocution.
Replacing these old panels is crucial not only to meet modern electrical standards but also to ensure the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system.
Symptoms of Panel Issues: Common Signs
Recognizing the early warning signs of panel issues can help you address problems before they escalate into more dangerous situations. Here are some common symptoms indicating that your circuit panel might need an upgrade:
- Flickering Lights: If lights flicker or dim frequently, it could indicate that your panel cannot handle the load or there are loose or faulty connections within the panel.
- Frequent Breaker Trips: Occasional trips can happen, but if breakers frequently trip, it’s a sign that your panel is overloaded or possibly failing.
- Burning Smells: A burning smell coming from your panel is a serious sign of an electrical short and should be addressed immediately to avoid potential fires.
- Corrosion or Rust: Any signs of corrosion or rust on the circuit breakers or within the panel box itself can compromise the safety of your electrical system.
- Overheating: If the panel or the wall area around it feels warm, or if the breakers are hot to the touch, your panel could be overloaded or failing.
Summation and Checklist for Recognizing the Need for a Panel Upgrade
Understanding the signs that your electrical panel needs an upgrade is crucial for maintaining the safety and functionality of your home’s electrical system. Use this checklist to routinely evaluate the condition and performance of your circuit panel:
- Visual Inspections:
- Regularly check for any visible signs of damage, such as rust, corrosion, or discoloration.
- Look for melted wires or scorch marks inside the panel.
- Functional Testing:
- Test circuit breakers periodically to ensure they are functioning properly. They should flip easily and firmly.
- Professional Evaluations:
- Schedule a comprehensive assessment with a licensed electrician if your home has an old panel or if you notice any of the above symptoms.
- Consider a full panel replacement if your home still has a Federal Pacific or Zinsco panel.
Addressing these issues promptly can help you avoid more significant and costly problems in the future, ensuring that your home remains a safe and comfortable place for you and your family.
Part 4: Upgrading Your Circuit Panel: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
The Upgrade Process: What Homeowners Should Expect
Understanding each step of the installation process can help you manage the project effectively:
Preparation and Safety Measures: Your electrician will prepare the work area, ensuring all safety protocols are in place. This includes turning off power to your home to avoid any electrical hazards.
Removal of the Old Panel: The existing circuit panel will be carefully dismantled and removed. This involves disconnecting all circuit breakers and ensuring that the wiring is properly labeled for reconnection to the new panel.
Installation of the New Panel: Your electrician will install the new panel, secure it to the wall, and connect the main power lines. Each circuit will then be connected to the new breakers, according to the previous labeling and any new configuration needed.
System Testing: Once the new panel is installed, your electrician will test each circuit to ensure everything is functioning correctly. This includes checking for proper installation, circuit load balancing, and the operation of new breakers.
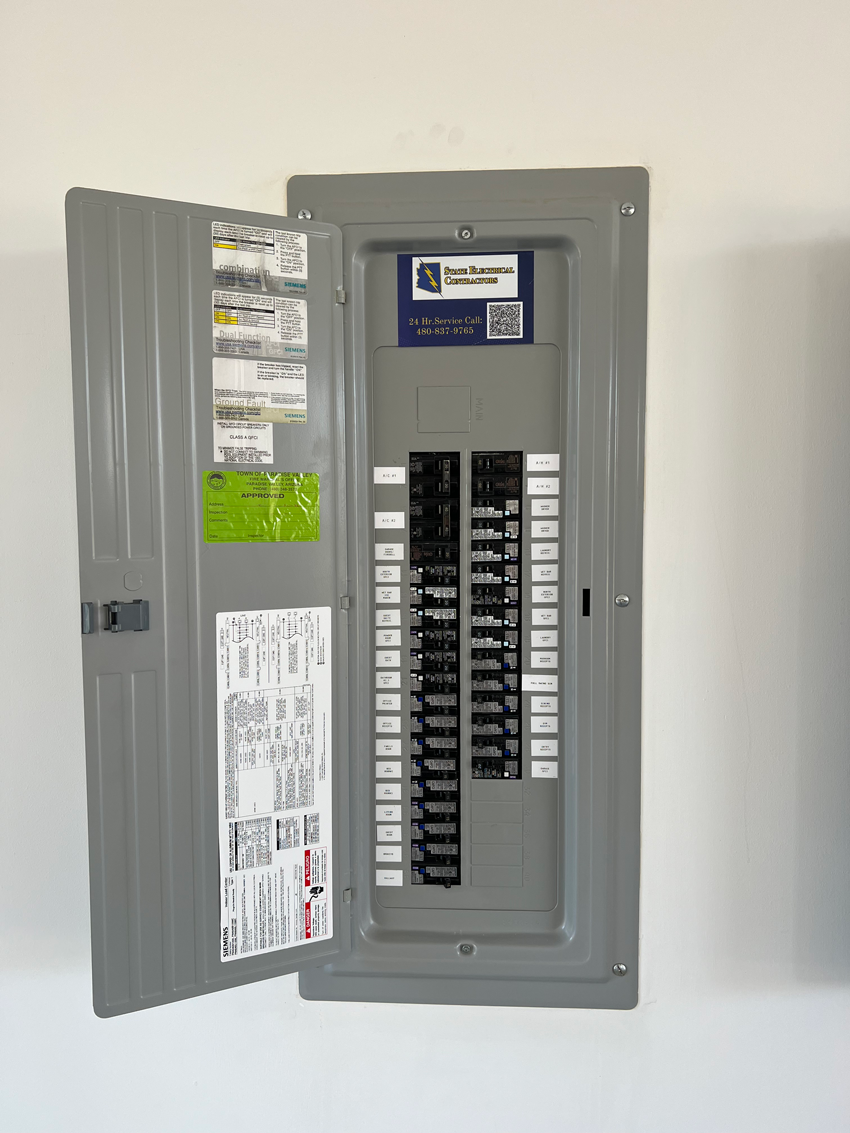

Final Inspection and Code Compliance: In many locations, a final inspection by a local official may be required to ensure the installation meets all electrical codes and safety standards. Your electrician should handle the coordination of this inspection and address any issues if they arise.
Power Restoration and Follow-Up: After passing inspection, power can be safely restored to your home. Your electrician might schedule a follow-up visit to ensure that the panel is functioning well under normal operating conditions.
Adding a Subpanel
In some cases, adding a subpanel to your home might be a more practical solution than upgrading your main circuit panel. Here’s what you need to know:
When to Consider a Subpanel: Adding a subpanel is beneficial when you need to extend the wiring and add circuits to different areas of your property, such as a new addition, a detached garage, or a workshop. It allows for better distribution of electrical loads and can simplify the management of your electrical system.
Benefits of a Subpanel:
- Enhanced Capacity: Provides additional circuit capacity without the need for a complete upgrade of your main panel.
- Localized Control: Allows for easier management and control of electrical circuits in specific areas of your home.
- Safety and Efficiency: Distributes electrical loads more evenly, reducing the risk of overloading the main panel and enhancing overall safety.
Installation Process: The installation of a subpanel involves similar steps to upgrading a main panel, including assessing electrical needs, ensuring compliance with local codes, and hiring a qualified electrician. The electrician will connect the subpanel to the main panel and distribute circuits as needed.
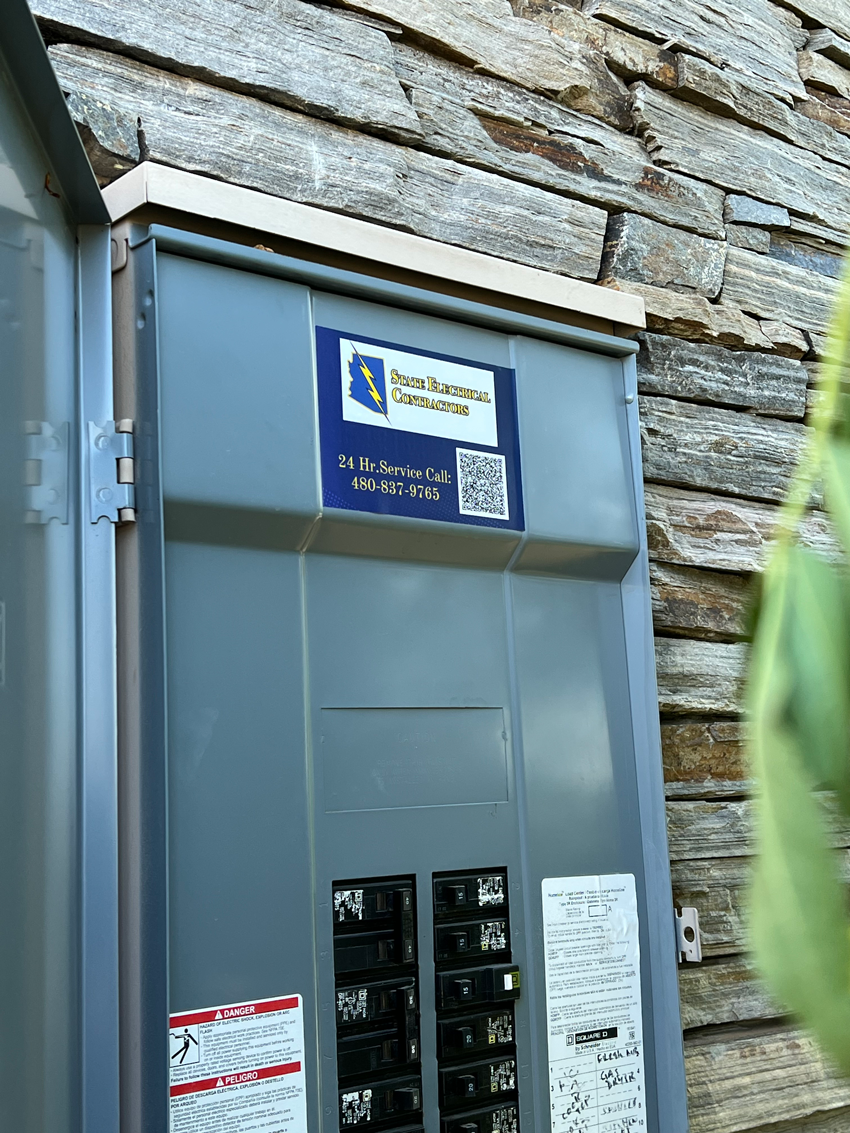

Choosing between upgrading your circuit panel and adding a subpanel depends on your specific needs and the condition of your existing electrical system. Upgrading the main panel enhances overall capacity and safety, while adding a subpanel can provide localized control and additional circuit capacity for specific areas.
For both upgrades and subpanel installations, it is crucial to work with experienced, licensed electricians who can ensure the work is done safely and in compliance with all relevant codes and standards. At State Electrical Contractors, we are committed to providing expert advice and high-quality electrical services to meet all your needs.
Part 5: Maintenance Tips for Your Electrical Panel
Maintaining your home’s electrical panel is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. Regular maintenance can help prevent unexpected issues and ensure your system operates at its best.
Regular Checks and Balancing: The Importance of Routine Maintenance
Regularly checking your electrical panel is essential for early detection of potential issues that could lead to more significant problems later. Here’s how and why you should perform these checks:
-
- Monthly: Open the panel door and visually inspect for any signs of damage, such as burn marks, rust, or loose connections. Check that all circuit breakers are firmly in place and not showing signs of wear or damage.
- Annually: Look for any discoloration or signs of overheating. Ensure that there are no open slots where dust and debris can enter.
-
- Biannually: Test each circuit breaker by flipping them off and on to ensure they are functioning correctly. This helps maintain mechanical functionality and confirms they are not stuck in the ‘on’ position.
-
- Review the distribution of your electrical loads across the circuit breakers to ensure no single circuit is overly burdened, which can lead to tripping and overheating.
-
- Ensure that all circuits are correctly labeled, reflecting their current use. This simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance.

Dealing with Common Issues: Practical Tips and Guidelines
Understanding how to address common electrical panel issues can save time and prevent safety hazards. Here are some tips on how to handle typical problems:
- Resetting a Tripped Breaker:
- When a breaker trips, it typically switches to a neutral position between ‘on’ and ‘off’. To reset, turn it fully off and then back on. If it trips again immediately, this indicates a persistent problem that needs professional attention.
- Testing Panel Functionality:
- Use a multimeter or voltage tester to check for proper output from each circuit. This helps ensure that all connections are secure and delivering the right voltage.
- Identifying When to Call a Professional:
- Persistent Issues: If a breaker frequently trips or if resetting doesn’t resolve the issue, it’s time to call a licensed electrician.
- Physical Damage: Any signs of damage or unusual conditions, such as buzzing noises from the panel or a burning smell, require immediate professional assessment.
- Upgrades or Modifications: Any work involving adding new circuits or significant changes to your electrical system should be handled by a professional to ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
Summation and Checklist for Maintaining Your Electrical Panel
Regular maintenance of your electrical panel is key to ensuring a safe and efficient home electrical system. Use this checklist to keep your panel in top condition:
- Monthly:
- Conduct a visual inspection for any obvious signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure the panel is free from obstructions and easily accessible.
- Biannually:
- Test all circuit breakers and safety switches to ensure functionality.
- Check and balance the load on your circuits.
- Annually:
- Have a professional electrician conduct a thorough inspection and perform any necessary maintenance.
- Review and update the labeling on your panel to reflect any changes in circuit functions.
Following these guidelines will help extend the life of your electrical panel and reduce the risk of electrical hazards, keeping your home safe and your system running efficiently.
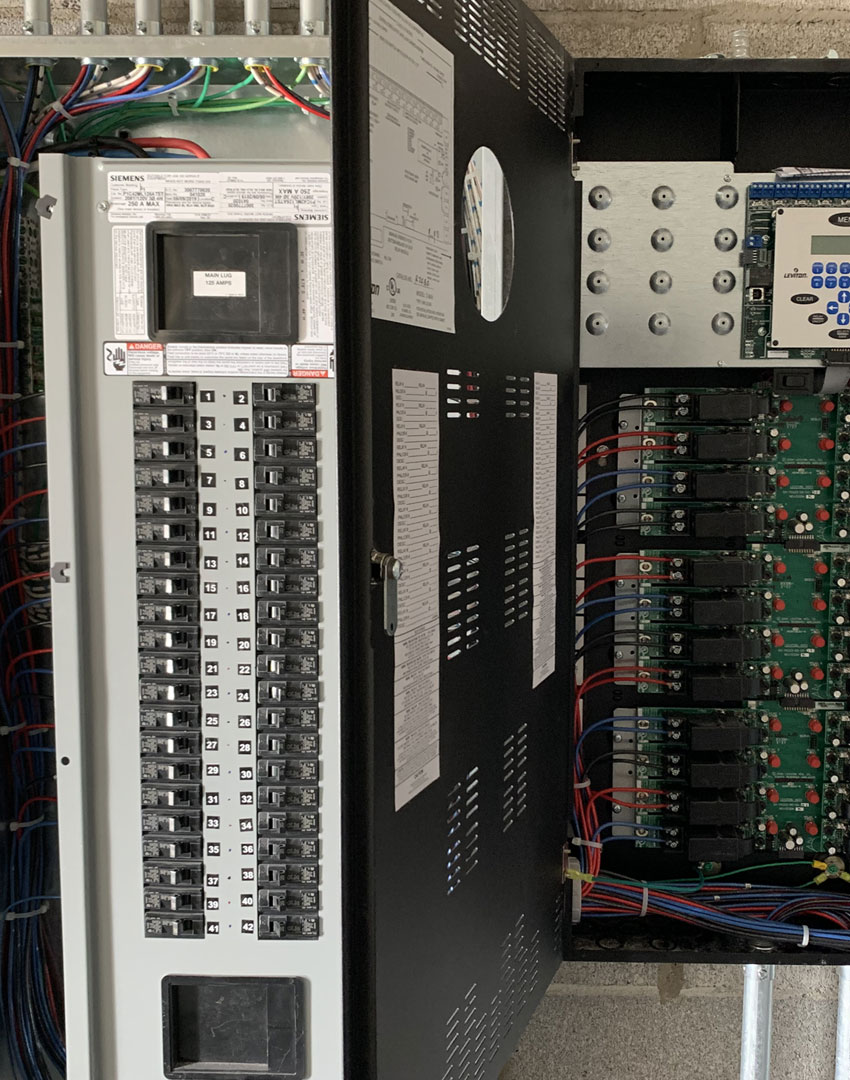
Part 6: Advanced Considerations for Your Electrical System
Enhancing your home’s electrical system with advanced technology can significantly improve its efficiency, safety, and convenience. Here’s a detailed look at two key upgrades: smart panels and surge protection.
Home Automation and Smart Panels: Enhancing Efficiency and Control
Smart panels represent the next generation of home electrical management, offering unparalleled control and monitoring capabilities. Here’s why you might consider upgrading:
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency:
- Smart panels provide detailed insights into your home’s energy consumption, allowing you to identify which appliances or systems are using the most power and when. This data can help you make informed decisions to reduce energy waste.
- Improved Safety Features:
- These panels can detect abnormal electrical behavior, such as unusual heat signatures or overloads, and can shut off power to specific circuits automatically, reducing the risk of electrical fires.
- Remote Monitoring and Control:
- With a smart panel, you can monitor and control your home’s electrical system remotely using a smartphone app. This is particularly useful for managing lighting, HVAC systems, and other appliances while away from home, ensuring that you never have to worry about leaving something on.
- Integration with Home Automation Systems:
- Smart panels can be integrated with broader home automation systems, allowing for scenarios like automatically adjusting power usage based on peak load times, which can save on electricity bills.
Surge Protection and Safety Enhancements: Securing Your Electrical Investments
Whole-home surge protectors are another critical upgrade for modern homes, especially as homes increasingly depend on sensitive electronics that are vulnerable to surge damage. Here’s how surge protection can benefit your home:
- Comprehensive Protection:
- Unlike power strips that only protect devices plugged directly into them, a whole-home surge protector is installed at the panel level, providing protection for all your home’s circuits and connected devices from external surges caused by lightning or utility fluctuations.
- Prolonged Appliance Lifespan:
- By smoothing out sudden spikes in voltage, whole-home surge protectors help extend the lifespan of your appliances and electronic devices, ensuring that they operate within safe electrical parameters.
- Cost-Effective:
- Investing in a whole-home surge protector can save money over time by avoiding the costs associated with repairing or replacing expensive electronics damaged by electrical surges.
- Added Resale Value:
- Homes with advanced electrical safety features like whole-home surge protectors are often more attractive to potential buyers, potentially increasing your home’s market value.
Summation and Checklist for Advanced Electrical System Upgrades
Upgrading to smart panels and installing whole-home surge protectors are forward-thinking choices that provide significant benefits. Here’s a quick checklist for considering these advanced options:
- Evaluate Your Needs:
- Assess the level of control and monitoring you desire for your home’s electrical system.
- Consider the value of the electronics and appliances you want to protect.
- Consult a Professional:
- Discuss with a licensed electrician the best options for smart panels and surge protectors based on your specific home layout and electrical needs.
- Plan for Installation:
- Schedule a professional installation to ensure that all components are correctly integrated into your existing system.
- Verify that all installations comply with local electrical codes and standards.
By considering these advanced upgrades, you can enhance your home’s electrical system to be more efficient, safe, and aligned with modern living standards, all while providing greater control and peace of mind.

Part 7: Local Laws and Codes in Maricopa County
Understanding and complying with local electrical laws and codes is crucial for ensuring the safety and legality of your home’s electrical system. This part provides a comprehensive overview of what Maricopa County homeowners need to know about local regulations and standards, and how to ensure that any electrical work meets these requirements.
Compliance and Safety: Key Local Regulations and Standards
Local electrical codes are designed to ensure safe installation practices and are typically based on the National Electrical Code (NEC) with local amendments. Here’s what you need to know about compliance in Maricopa County:
- Permit Requirements:
- Most electrical work in Maricopa County, including upgrades, significant repairs, and new installations, requires a permit. This ensures that all work is inspected and approved as safe and up to code by local authorities.
- Specific Local Amendments:
- Maricopa County may have specific amendments to the NEC that address local safety concerns, such as requirements for higher-rated electrical components due to higher temperatures or additional grounding measures.
- Regular Code Updates:
- Electrical codes are updated regularly to incorporate new safety technologies and practices. Homeowners and professionals should check for the latest requirements to ensure compliance for any new projects.
- Safety Inspections:
- After any significant electrical work, a safety inspection is typically required to ensure the installation meets local codes. These inspections are crucial for preventing future electrical hazards.
Hiring and Compliance: Ensuring Code Adherence
When upgrading or modifying your home’s electrical system, it’s vital to ensure that all work performed by electricians adheres to local codes. Here’s how to ensure compliance:
- Hire Licensed Professionals:
- Always hire a licensed electrician who is familiar with Maricopa County’s specific codes and requirements. Licensed professionals are required to stay updated on all local laws and are more likely to ensure compliance in their work.
- Verify Permits:
- Before any work begins, verify that your electrician has obtained all necessary permits. This not only ensures legality but also guarantees that the work will be inspected by a county official.
- Ask for Detailed Plans:
- Request a detailed plan or blueprint of the proposed work, which should outline how the project will comply with local codes. This is particularly important for major upgrades or new installations.
- Attend Inspections:
- Whenever possible, be present during the final inspection. This allows you to ensure that all work has been approved and any issues are addressed promptly.
- Maintain Documentation:
- Keep records of all permits, inspection reports, and work receipts. This documentation can be valuable for insurance purposes, future property sales, or resolving any potential legal issues.
Summation and Checklist for Navigating Local Laws and Codes
Understanding and adhering to local electrical laws and codes is essential for maintaining a safe and legally compliant home. Use this checklist to navigate the legal landscape of your electrical system upgrades:
- Check for Updates:
- Regularly consult Maricopa County’s building and safety department website for updates on local electrical codes.
- Pre-Work Checklist:
- Ensure your electrician secures the necessary permits.
- Confirm that the electrician’s plan adheres to all local amendments to the NEC.
- Post-Work Checklist:
- Ensure all work is inspected and approved.
- Keep a file with all related documents for future reference.
By diligently following these guidelines, you can ensure that all electrical work in your home not only enhances its functionality and safety but also fully complies with Maricopa County’s stringent regulations.

Part 8: FAQ and Troubleshooting Guide
Addressing common questions and providing basic troubleshooting tips can empower homeowners to manage their electrical systems more effectively. This section offers insights and practical advice to help you navigate common issues related to electrical panels and service.
Common Questions: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Electrical Panels and Service
- What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
- A circuit breaker is a switch that automatically turns off when it detects an overload or short circuit. It can be reset and reused. A fuse contains a thin metal wire that melts and disconnects the circuit in overload conditions, requiring replacement.
- How often should my electrical panel be inspected?
- It’s recommended to have a professional inspection at least every three to five years, or immediately if you purchase a home with an older electrical system, to ensure everything is up to code and functioning safely.
- Can I add more circuits to my existing electrical panel?
- Yes, but only if there is physical space for additional circuit breakers and your panel’s capacity can handle the increased load. It’s best to consult with a licensed electrician to assess and possibly upgrade your panel.
- What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
- Frequent tripping can indicate an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, or a faulty breaker. Identify and unplug the appliances causing the overload, check for any obvious short circuits, or consider replacing the breaker if it appears defective.
- Is it safe to replace a circuit breaker myself?
- Replacing a circuit breaker involves working inside the electrical panel, which can be dangerous if not done correctly. It’s recommended to hire a licensed electrician for this task to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
Troubleshooting Tips: Basic Troubleshooting Homeowners Can Safely Perform
- Resetting Tripped Breakers:
- If a breaker trips, turn off all appliances on that circuit, reset the breaker by switching it to the OFF position and then back to ON. If it trips again, leave it off and call an electrician.
- Identifying Overloaded Circuits:
- If breakers frequently trip when using certain appliances, you might be overloading the circuit. Try redistributing high-energy appliances to different circuits or reduce the number of appliances used simultaneously.
- Checking for Faulty Outlets:
- Use a multimeter or a simple outlet tester to check for proper functioning. If an outlet is not working, check if the corresponding breaker has tripped. If the outlet still doesn’t work after resetting the breaker, it may need replacement.
- GFCI Testing:
- Test all GFCI outlets monthly by pressing the “Test” button. The power should cut off immediately. Press the “Reset” button to restore power. If it doesn’t test properly, replace the GFCI outlet.
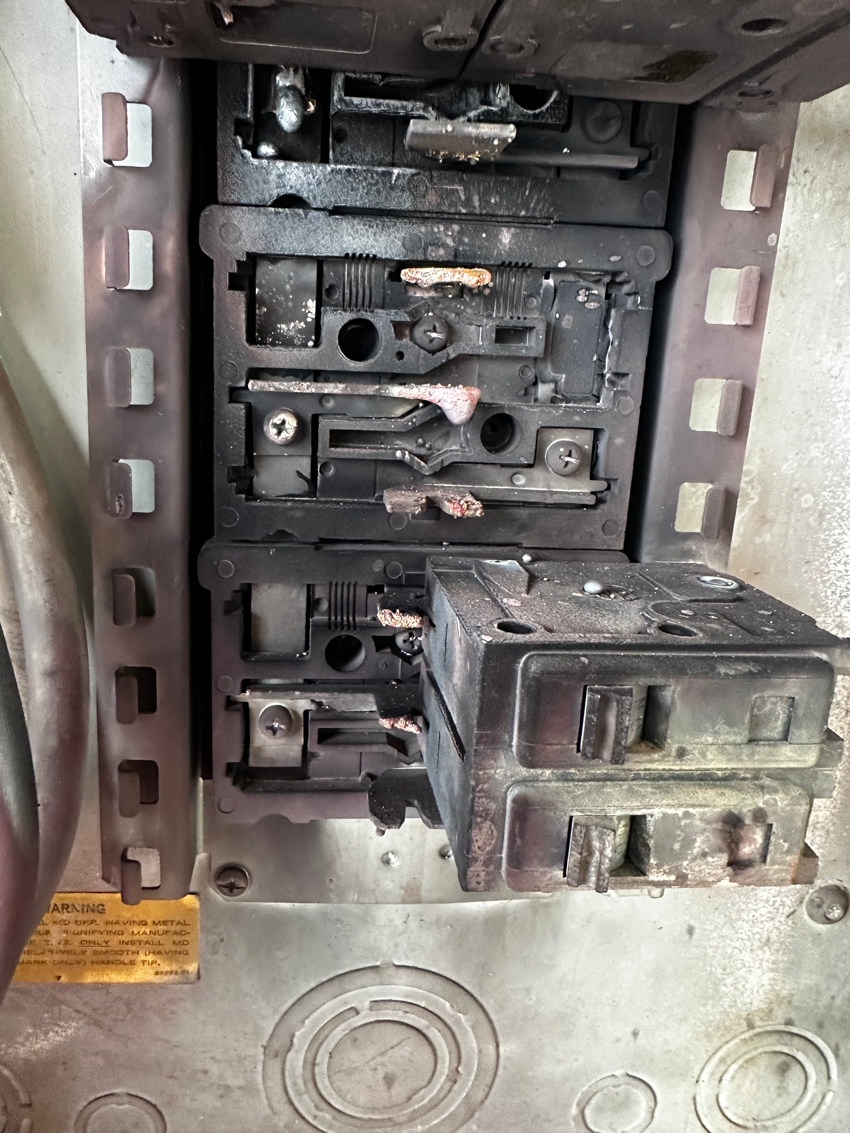
- Inspecting for Visible Damage:
- Regularly inspect your electrical panel for any signs of wear, rust, or damage. Look for discolored or burnt areas on the panel or wiring. Do not touch any of the components; if damage is visible, contact a professional.
Summation and Checklist for Troubleshooting
Having a set of troubleshooting guidelines can help you address minor issues safely and identify when professional help is needed. Here’s a quick checklist for basic troubleshooting:
- Regular Checks:
- Perform visual inspections and testing of GFCI outlets and circuit breakers regularly.
- Keep track of any appliances or devices that frequently cause breaker trips.
- When to Call a Professional:
- If issues persist after your initial troubleshooting.
- For any modifications, replacements, or upgrades to your electrical panel.
By familiarizing yourself with these FAQs and troubleshooting tips, you can better understand and manage your home’s electrical system, ensuring safety and efficiency while minimizing the need for costly professional interventions for common issues.
Part 9: Glossary of Terms and Resources
Addressing common questions and providing basic troubleshooting tips can empower homeowners to manage their electrical systems more effectively. This section offers insights and practical advice to help you navigate common issues related to electrical panels and service.
Common Questions: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Electrical Panels and Service
- What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
- A circuit breaker is a switch that automatically turns off when it detects an overload or short circuit. It can be reset and reused. A fuse contains a thin metal wire that melts and disconnects the circuit in overload conditions, requiring replacement.
- How often should my electrical panel be inspected?
- It’s recommended to have a professional inspection at least every three to five years, or immediately if you purchase a home with an older electrical system, to ensure everything is up to code and functioning safely.
- Can I add more circuits to my existing electrical panel?
- Yes, but only if there is physical space for additional circuit breakers and your panel’s capacity can handle the increased load. It’s best to consult with a licensed electrician to assess and possibly upgrade your panel.
- What should I do if my circuit breaker keeps tripping?
- Frequent tripping can indicate an overloaded circuit, a short circuit, or a faulty breaker. Identify and unplug the appliances causing the overload, check for any obvious short circuits, or consider replacing the breaker if it appears defective.
- Is it safe to replace a circuit breaker myself?
- Replacing a circuit breaker involves working inside the electrical panel, which can be dangerous if not done correctly. It’s recommended to hire a licensed electrician for this task to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
Troubleshooting Tips: Basic Troubleshooting Homeowners Can Safely Perform
- Resetting Tripped Breakers:
- If a breaker trips, turn off all appliances on that circuit, reset the breaker by switching it to the OFF position and then back to ON. If it trips again, leave it off and call an electrician.
- Identifying Overloaded Circuits:
- If breakers frequently trip when using certain appliances, you might be overloading the circuit. Try redistributing high-energy appliances to different circuits or reduce the number of appliances used simultaneously.
- Checking for Faulty Outlets:
- Use a multimeter or a simple outlet tester to check for proper functioning. If an outlet is not working, check if the corresponding breaker has tripped. If the outlet still doesn’t work after resetting the breaker, it may need replacement.
- GFCI Testing:
- Test all GFCI outlets monthly by pressing the “Test” button. The power should cut off immediately. Press the “Reset” button to restore power. If it doesn’t test properly, replace the GFCI outlet.
- Inspecting for Visible Damage:
- Regularly inspect your electrical panel for any signs of wear, rust, or damage. Look for discolored or burnt areas on the panel or wiring. Do not touch any of the components; if damage is visible, contact a professional.
Summation and Checklist for Troubleshooting
Having a set of troubleshooting guidelines can help you address minor issues safely and identify when professional help is needed. Here’s a quick checklist for basic troubleshooting:
- Regular Checks:
- Perform visual inspections and testing of GFCI outlets and circuit breakers regularly.
- Keep track of any appliances or devices that frequently cause breaker trips.
- When to Call a Professional:
- If issues persist after your initial troubleshooting.
- For any modifications, replacements, or upgrades to your electrical panel.
By familiarizing yourself with these FAQs and troubleshooting tips, you can better understand and manage your home’s electrical system, ensuring safety and efficiency while minimizing the need for costly professional interventions for common issues.