Circuit Panels & Your Arizona Home.
Understanding Your Home’s Power Portal
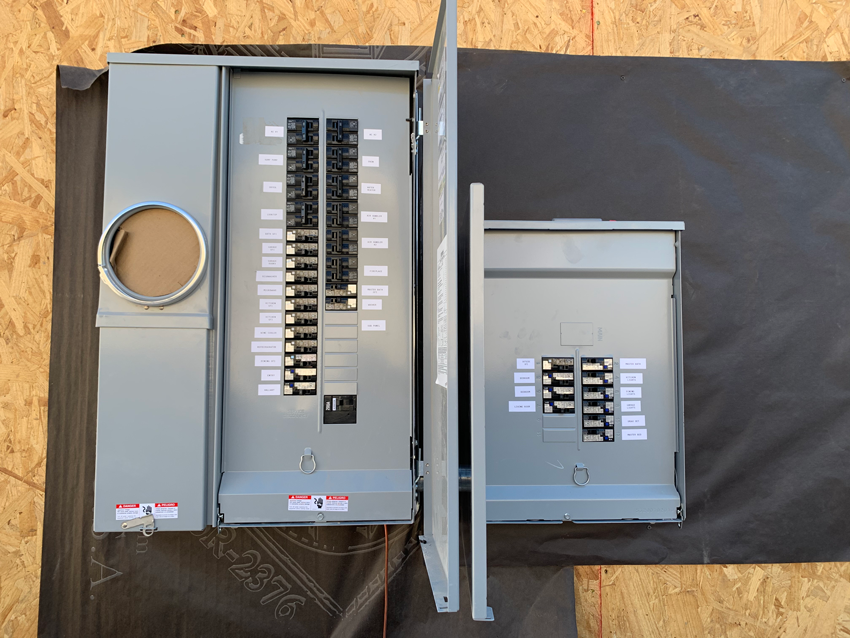
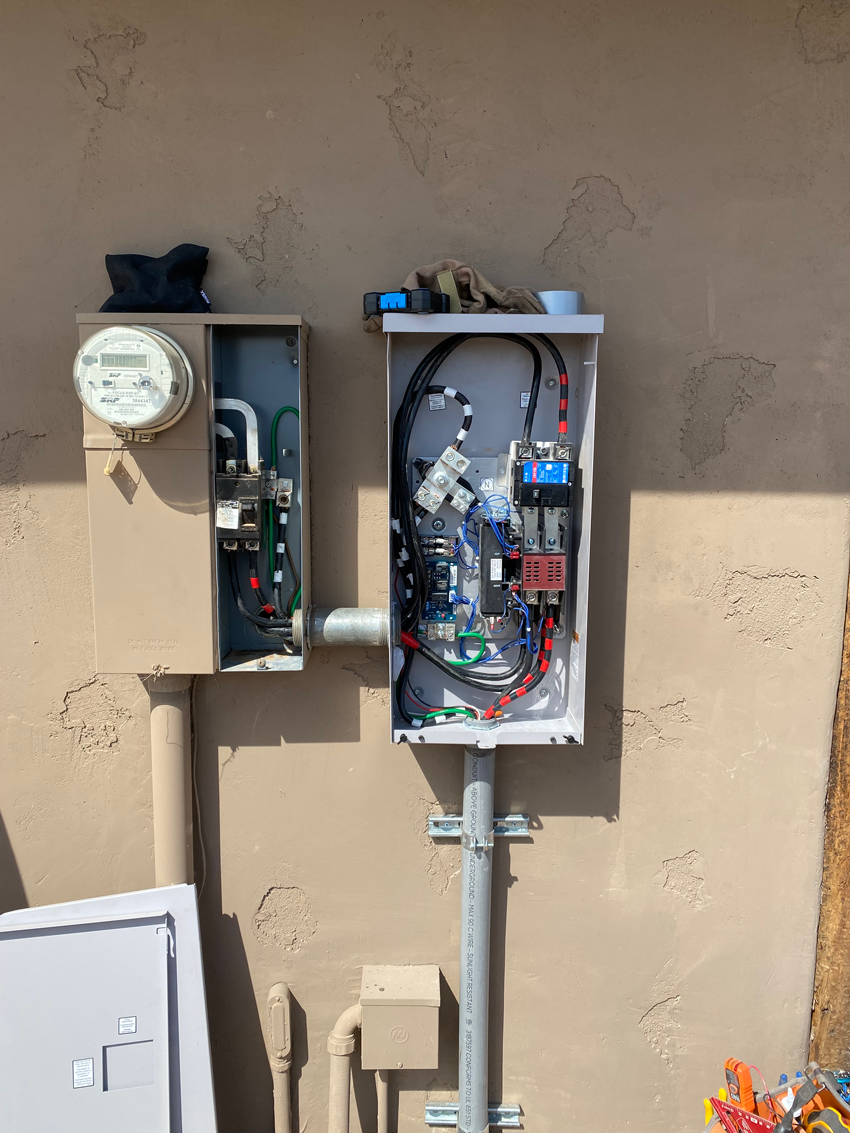
A breaker box, also known as a panel box, breaker panel, electric panel, or service panel, is the central hub of a home’s electrical system. It is responsible for distributing electricity to all of the circuits in the home, and it also contains safety devices that protect the home from electrical hazards. The breaker box is typically located in a utility room or closet.
Homeowners should have a basic understanding of their home’s electrical system, starting with the breaker box.
Your Phoenix AZ Breaker Box Location:
Residential circuit breaker boxes are typically placed outside of homes in Maricopa County, Arizona, primarily due to local building codes and environmental considerations. Here are some reasons why:
- Building Codes and Regulations: Local building codes in Maricopa County may require that electrical panels be accessible to utility workers and emergency responders without them having to enter the home. This ensures that in case of an emergency, such as a fire or electrical hazard, the power can be quickly and safely shut off.
- Ease of Access for Maintenance and Inspection: Placing the circuit breaker box outside allows for easier access by electricians for maintenance and inspections. This is convenient for homeowners as it doesn’t require them to be home for such services.
- Environmental Factors: Arizona’s climate is generally dry and less prone to the types of moisture issues that can affect electrical systems in more humid climates. Having the breaker box outside is less of a risk in terms of moisture-related damage.
- Heat Dissipation: Arizona is known for its high temperatures, especially in Maricopa County. Having the breaker box outside may help in dissipating heat generated by the electrical system, reducing the risk of overheating.
- Space Considerations: Homes in Maricopa County, like many in the Southwest, often have specific architectural styles and layouts. Placing the breaker box outside can help save indoor space, which is particularly beneficial in smaller homes or those with specific design constraints.
These reasons combine practicality, safety, and adherence to local building standards, making it a common practice in our local region. It also provides an extra layer of safety to have the breaker box outside of your home.
Now that you have located your home’s circuit panel, let’s move on to the most important concept in your home’s electrical system.





Personal Safety When Working With Your Home’s Patch Panel!
When working with your home’s electrical system in Phoenix, AZ, or anywhere else, safety is paramount. Here are some important safety measures to consider:
Turn Off Power: Before starting any electrical work, always turn off the power to the circuit you’re working on at the main breaker box. This is crucial to prevent electric shock. If you are unsure of how to turn off a specific circuit, contact the pros at State Electrical Contactors for your electrical inspection. We’ll label the circuits for you so that turning one off won’t be a frustration factor.
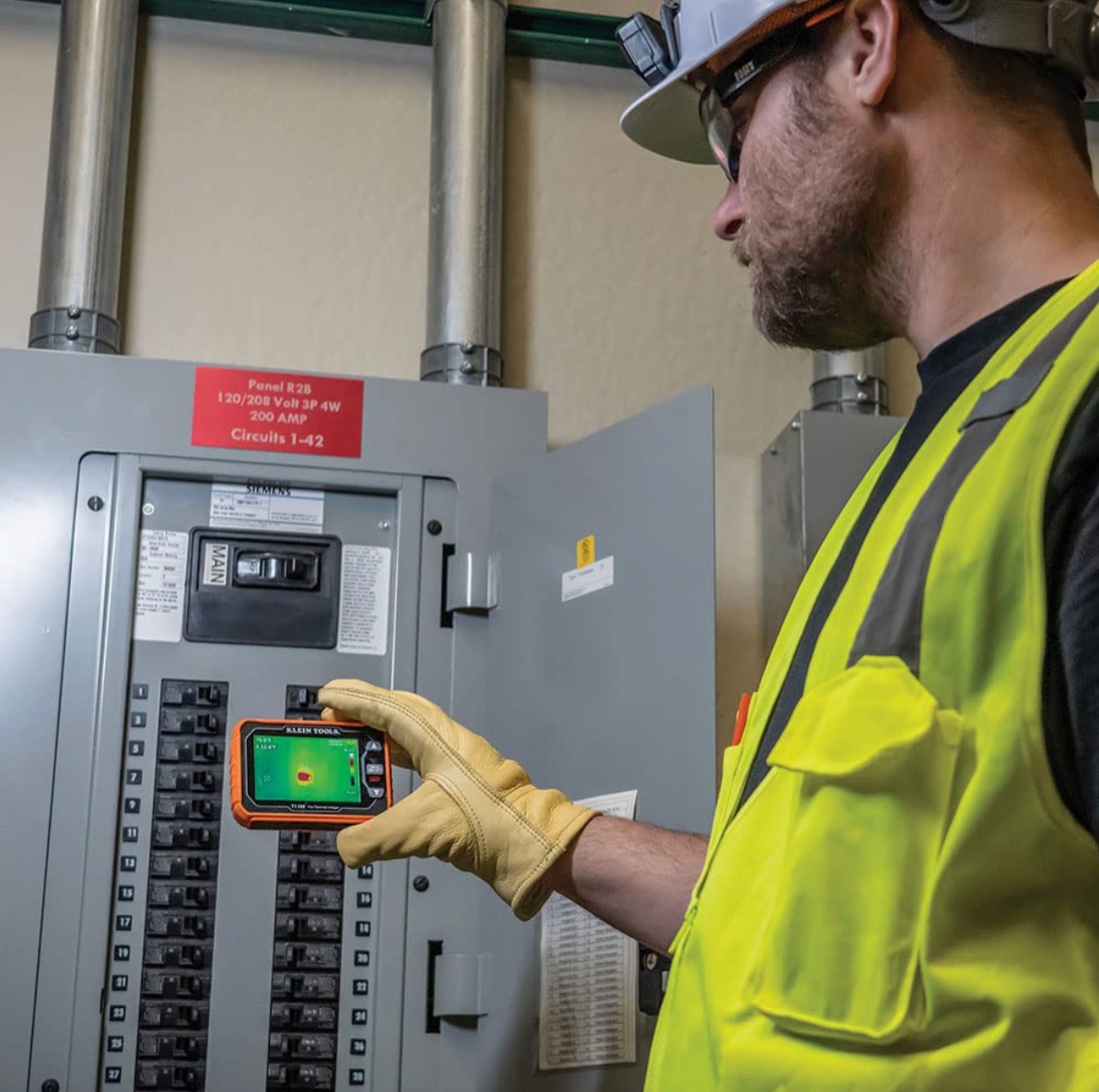
Use a Voltage Tester: After turning off the power, use a voltage tester on the wires you’ll be working with to ensure there is no current flowing through them.
A voltage tester is an electrical tool used to detect the presence of voltage in a circuit. It is a basic piece of electrical safety equipment that can help to prevent electrical shocks. There are two main types of voltage testers: contact voltage testers and non-contact voltage testers.
Wear Appropriate Safety Gear: Wear rubber-soled shoes to reduce the risk of grounding a current, and consider using insulated gloves and safety goggles for added protection.
We know that most folks wear sneakers, or rubber soled shoes, however it still needs to be said. Especially when it revolves around the topic of personal safety.
Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, so never work on electrical components in wet or damp conditions. This includes sweating, which can increase the risk of electric shock. It may sounds strange, it’s better to err on the side of caution.
Use Insulated Tools: When working with electrical components, use tools with insulated handles to reduce the risk of shock. This is a good time to step back and ask yourself if you need to contact a licensed electrician at State Electrical Contractors.
Stay Informed about Local Codes: Be aware of the local building and electrical codes in Maricopa County and Phoenix, AZ. Adhering to these codes is crucial for both safety and legal compliance. It can also help you avoid fines.
Be Cautious with Aluminum Wiring: Some older homes in Phoenix may have aluminum wiring, which can be more hazardous than copper. It’s important to know the specific considerations for working with aluminum. Check out our post about swapping out your home’s aluminum wiring.
Secure a Permit if Necessary: For major electrical work, a permit might be required. This ensures that your work is inspected and meets local safety standards.
Always Consider Professional Help: If you’re not confident in your ability to safely complete the work, it’s best to hire a licensed electrician. Electrical work can be dangerous, and professionals are trained to handle these risks.
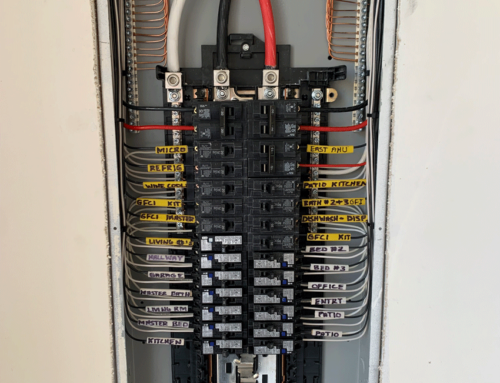
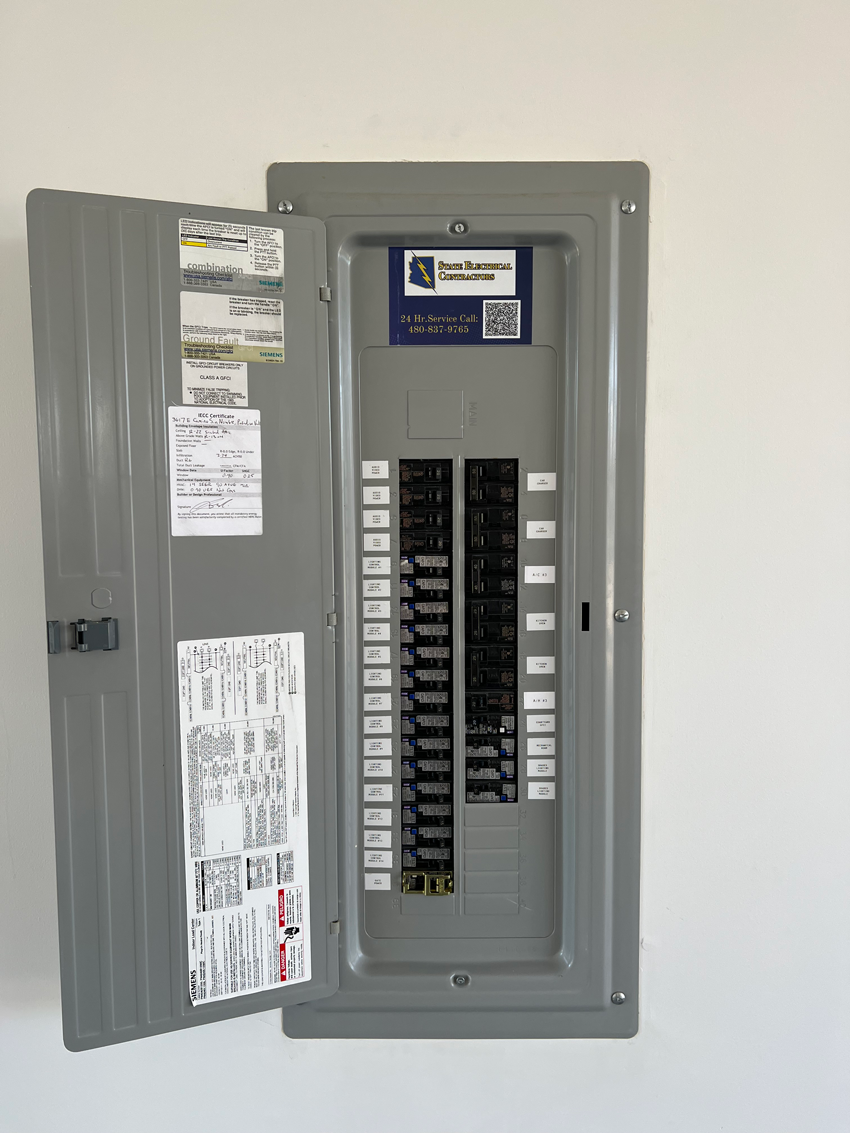
What’s Behind The Door Of Your Home’s Circuit Breaker Panel?
The main components of a circuit breaker panel include:
- Main breaker: The main breaker is the largest breaker in the panel and it controls the flow of electricity to all of the other breakers in the panel.
- Branch breakers: Branch breakers are smaller breakers that control the flow of electricity to individual circuits in the house. Each circuit is responsible for powering a specific group of outlets or appliances.
- Bus bars: Bus bars are copper or aluminum bars that distribute electricity to the breakers in the panel. There are two bus bars in a circuit breaker panel: a hot bus bar and a neutral bus bar.
- Grounding wire: The grounding wire is a green or bare copper wire that connects the panel to the ground. The grounding wire is important for safety because it helps to prevent electrical shock.
- Labels: Each breaker in the panel should be labeled with the circuit that it controls. This helps to make it easy to identify which breaker to trip if a circuit overloads.
In addition to these main components, some circuit breaker panels may also have other features, such as a surge protector or a generator hookup. These features can help to protect the electrical system from damage and provide power during an outage.
s better to err on the side of caution.